
Each factor has two levels and there are four treatments in total.
#Doe minitab full
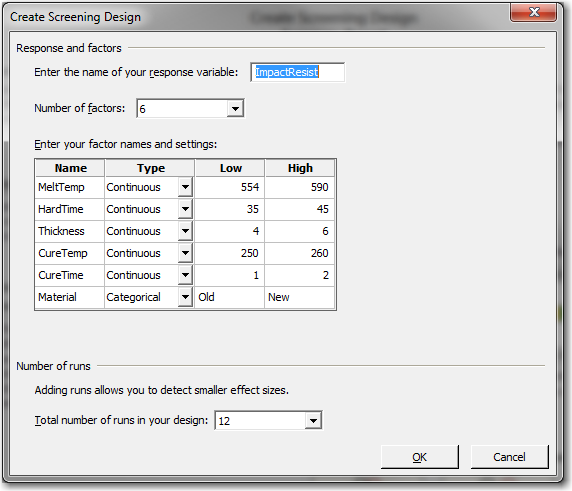
2 2 Full Factorial DOEĬase study: We are running a 2 2 full factorial DOE to discover the cause-and-effect relationship between the cake tastiness and two factors: temperature of the oven and time length of baking. Advantages of replication include: helps to better identify the true sources of variation, helps estimate the true impacts of the factors on the response, and overall improves the reliability and validity of the experimental results. The order to run the treatments in an experiment should be randomized to minimize the noise. Replicates are the number of repetitions of running an individual treatment, which increase the power of the experimental responses. Replication in ExperimentsĮach treatment can be tested multiple times in an experiment in order to increase the degrees of freedom and improve the capability of analysis. When actually running the experiments, randomizing the standard order is recommended to minimize the noise. Standard order is used to design the combinations/treatments before experiments start.
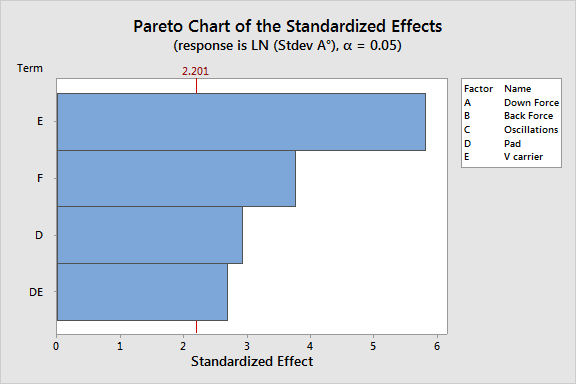
The four design patterns shown earlier are listed in the standard order. Two-Level Four-Factor Full Factorialīelow is a design pattern of a two-level four-factor full factorial experimentĢ (levels) raised to 4 (factors) = 16 treatment combinations Two-Level Five-Factor Full Factorialīelow is a design pattern of a two-level five-factor full factorial experimentĢ (levels) raised to 5 (factors) = 32 treatment combinations Order to Run Experiments Two-Level Three-Factor Full Factorialīelow is a design pattern of a two-level three-factor full factorial experiment.Ģ (levels) raised to 3 (factors) = 8 treatment combinations. α pare the coefficients of the factors and interactionsīelow is a design pattern of a two-level two-factor full factorial experiment.Ģ (level) raised to 2 (factors) = 4 treatment combinations. Generate an equation to describe the relationship between Y and the important Xs:
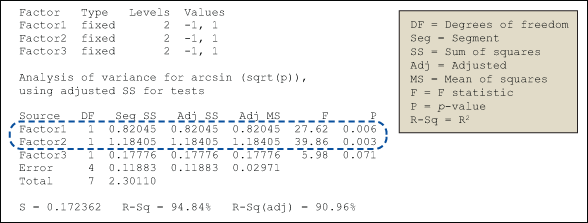
For example, for two-level design (i.e.each factor has two levels) with k factors, there are 2k possible scenarios or treatments. In a full factorial experiment, all of the possible combinations of factors and levels are created and tested.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
